EMS and microcurrent are both non-invasive electrical treatments, but they serve different purposes. EMS uses electrical impulses to contract muscles, helping you build strength and tone. Microcurrent, on the other hand, stimulates skin cells at a cellular level to promote skin rejuvenation and reduce wrinkles. While EMS focuses on muscle enhancement, microcurrent targets surface improvements. To understand how each can work best for you and where they overlap, keep exploring the details ahead.
Key Takeaways
- EMS stimulates muscle contractions to build strength, while microcurrent promotes skin repair at the cellular level.
- EMS targets deeper muscle tissues; microcurrent primarily affects surface skin layers.
- EMS enhances muscle tone and definition; microcurrent improves skin firmness and reduces wrinkles.
- EMS is used for muscle rehabilitation and toning; microcurrent focuses on facial rejuvenation and skin health.
- Both are non-invasive and painless, but serve different aesthetic and functional purposes.
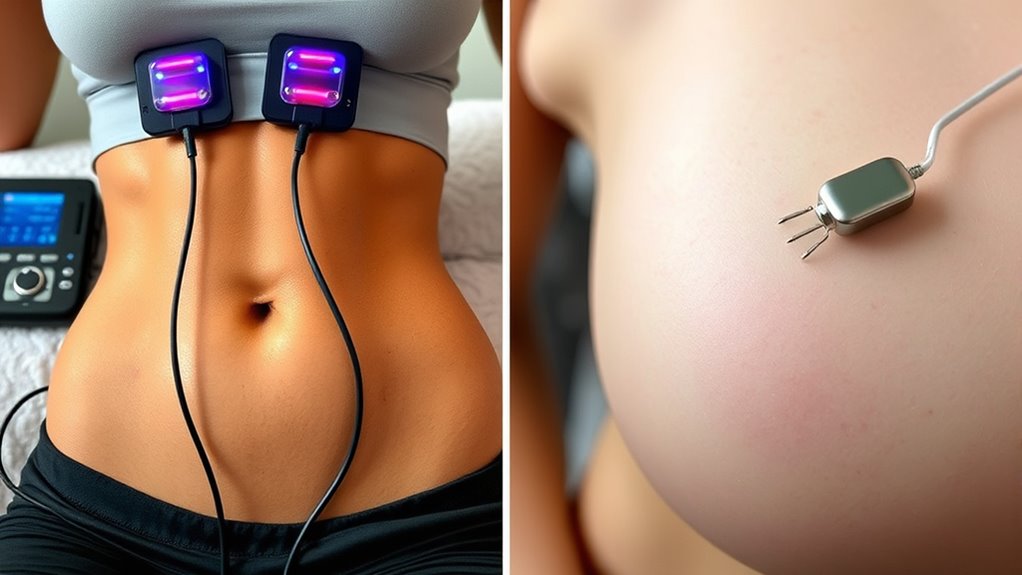
If you’re considering non-invasive options to improve muscle tone and skin appearance, understanding the differences between EMS and microcurrent therapy is essential. Both methods utilize electrical stimulation, but they target different outcomes through distinct mechanisms. EMS, or Electrical Muscle Stimulation, primarily focuses on muscle stimulation. When you undergo EMS, small electrical impulses activate your muscle fibers, causing them to contract similarly to how they do during exercise. This process helps strengthen and tonify muscles without physical activity, making it a popular choice for muscle building, rehabilitation, or maintaining muscle mass. You might notice your muscles feeling firmer after a session, and over time, this can translate into more defined contours. EMS is especially effective for areas where you want to improve muscle strength or combat muscle atrophy.
On the other hand, microcurrent therapy centers around skin rejuvenation. This technique delivers very low-level electrical currents that mimic your body’s natural bioelectric signals. When you receive microcurrent treatments, these gentle currents penetrate the skin, stimulating your cells at a cellular level. The result is increased production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is essential for cellular repair and regeneration. This process boosts collagen and elastin production, key proteins responsible for skin firmness and elasticity. As a result, microcurrent therapy can reduce fine lines, improve skin tone, and give your complexion a more youthful glow. It’s often used as a facial treatment, but it also benefits other areas where skin sagging or dullness are concerns. Additionally, understanding AI-driven diagnostics can enhance treatment precision and outcomes.
While EMS is more about strengthening muscles beneath the skin, microcurrent therapy is focused on skin health and surface rejuvenation. Both treatments are non-invasive, painless, and carry minimal risks, but they serve different goals. If you’re after a more sculpted look and muscle definition, EMS might be your best fit. If your main concern is improving skin texture, reducing wrinkles, or lifting sagging skin, microcurrent therapy could be more suitable. Some clinics even combine both techniques for holistic results, targeting muscle tone and skin rejuvenation simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can EMS and Microcurrent Be Used Together Effectively?
Yes, you can use EMS and microcurrent devices together effectively if the devices are compatible and follow proper treatment protocols. Always check device compatibility to make certain they can be used in tandem without interference. Stick to established treatment protocols, alternating or combining sessions as recommended. This approach can maximize benefits like muscle toning and skin rejuvenation, but consulting a professional ensures safe, effective results tailored to your goals.
Are There Any Side Effects of Long-Term Use for Either Technology?
Long-term use of EMS and microcurrent generally has low side effect risks, but it’s important to take into account long-term safety. You might experience skin irritation or muscle fatigue if used excessively or improperly. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and consult a healthcare professional if you notice persistent discomfort. Regularly monitoring your response helps ensure safe, effective results without risking adverse side effects from prolonged use.
How Do EMS and Microcurrent Differ in Pain Management?
Think of EMS like a gentle workout for your muscles, stimulating them to reduce pain through muscle stimulation and improved blood flow. Microcurrent, however, acts like a tiny healer, promoting pain relief by stimulating cellular repair at a microscopic level. You might notice EMS more effective for muscle soreness, while microcurrent targets nerve pain and inflammation. Both methods help manage pain, but they do so through different mechanisms tailored to your needs.
What Are the Cost Differences Between EMS and Microcurrent Devices?
You’ll find that EMS devices typically cost more upfront due to their advanced technology and durability, but their maintenance costs are moderate because of solid build quality. Microcurrent devices tend to be less expensive initially but may require more frequent replacements or repairs, increasing long-term costs. Consider your budget and ongoing maintenance needs when choosing between the two, and remember that device durability impacts both purchase price and upkeep expenses.
Which Therapy Is More Suitable for Athletes’ Recovery?
Think of your recovery as tending a garden—EMS acts like a diligent gardener, activating muscles and promoting circulation, speeding up healing. Microcurrent, like gentle watering, supports tissue repair on a cellular level. For athletes, EMS is more suitable for muscle activation and circulatory improvement, helping you bounce back faster after intense workouts. Its targeted approach guarantees you recover efficiently, ready to seize your next challenge.
Conclusion
Now that you understand the differences between EMS and microcurrent, you can choose what’s best for your goals. For example, if you’re aiming to tone your muscles quickly, EMS might be your go-to. Imagine someone recovering from an injury using microcurrent to promote healing without pain—it’s all about matching the technology to your needs. Whether for fitness or recovery, knowing these differences helps you make smarter, more effective choices for your body.